Introduction to Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
Over the past few years, Robotic process automation has become a popular technology for many organizations. RPA is a program/software mimicking human actions to perform a sequence of steps with or without human intervention to achieve a business process. From order creation to delivery, the RPA bot can update customers to keep them in the loop. Bots can also be used as customer service chatbots. They can be configured to respond in chats with the customer to address simple questions or even initiate returns. The customer support team can concentrate on more critical customer issues with these bots.
What is Test Automation?
Test automation is automating the testing procedure with a set of programs. Test Automation is usually done with some of the Testing Tools available in the market, following an Automation Framework. This automation code takes care of executing the Tests automatically, handling the Test data, and providing Test results, giving good insights into the quality of the software. This expedites the testing process by identifying the issues/defects and thereby helps improve the application quality.
Benefits of RPA vs. Test Automation
| RPA | Test Automation |
| Applied to business processes and products | Applied to a product/application |
| RPA aims to make a process work | It aims at testing various functionalities that could break a process |
| It does not require much coding skills | Require more coding skills |
| Built to automate specific tasks within a sequence | Designed to measure the resilience of a broader sequence of tasks |
| Creates a process flow for the software “robot” to follow with limited capabilities across the Testing stages | Supports all Testing stages; with a strong focus on support for continuous testing |
| Various stakeholders can use it | Limited to Testing stakeholders |
| RPA tools are expected to run on the business production environment to achieve business objectives. | Test automation tools are intended to validate whether an IT application performs per the given specification. |
How Robotic Process Automation Works
Jobs that require complex calculations, accuracy, data analysis, and recording, especially any job that requires replicating a human action, are done more efficiently through RPA. In a rapidly changing world with growing industrial and business segments and their operations relying on automation, RPA has been a boon in recent years, from flying unmanned flights to complex surgeries on humans.
RPA came into business from the below three predecessors:
- Screen Scrapping
- Workflow Automation
- Artificial Intelligence
Screen Scrapping: This plays a significant role in the fields of data migration and data integration. It connects between legacy and current systems. This collects the data from one application, translates it, and displays it through another application.
Workflow Automation: Automation and execution of the business process is entirely based on a set of predefined rules. This helps reduce the effort of execution and optimize workflow.
Artificial Intelligence: This concept deals with stimulating the human intelligence of machines. This helps transform industry and business. The combined form of Automation and Artificial Intelligence is RPA.

How Test Automation Works
Test Automation focuses on replacing repetitive manual Testing tasks with a system that enhances efficiency. Test Pyramid is a simple rule of thumb to get this right. It is a framework that defines various types of tests and how many times they should appear. Test Pyramid tells us how much testing is required on each layer.
The Test Pyramid consists of three different layers:
- Base Layer – Unit Tests
- Middle Layer – Service/API Layer Tests (Integration Tests)
- Top Layer – User Interface Tests
Test Automation refers to executing test cases and comparing the results with the expected results.
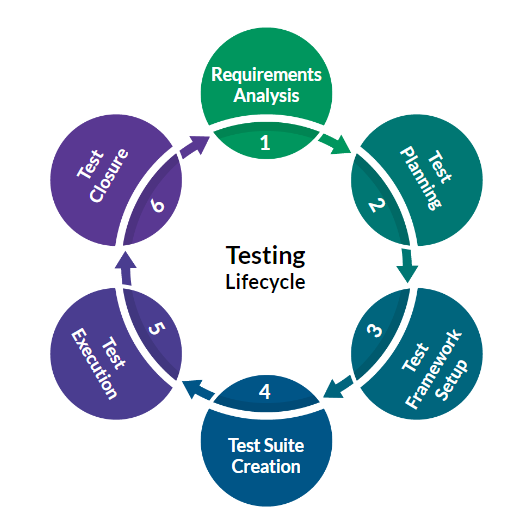
Generally, Test Automation involves four significant steps, which are as follows:
- Define the Scope of Automation: It defines the application functionalities that need to be tested and are feasible for Automation.
- Choosing the right tool: Selecting a tool depends on various factors, from the underlying technology on which the application is built to the scope of the test that we intend to perform.
- Plan, Design, and Develop (Automation Strategy and Plan): This phase includes Framework design and features, Scheduling timelines, Test Suite preparation, Test data setup, etc.
- Execution of Test Cases: In this phase, automated Test scripts are executed, and the results captured are analyzed. A final Test closure report is prepared and shared with all the stakeholders.
Conclusion
Test Automation tools are built for specific products or application types such as web, mobile, or desktop, and RPA can be applied to processes, so they are not bounded and can be customized based on requirements. User acceptance Tests have been more accurate and effective with RPA, which is one reason why RPA is considered a new power tool for testing. It’s more than what kind of tool we use; how efficiently we use it determines the success or failure of our attempt. Although both Test Automation and RPA reduce manual intervention and improve the quality of the outcome within less time, the extent of use for both processes varies greatly.
If you are looking for testing-related solutions, XTIVIA’s Testing Center of Excellence is available to help you with your projects.
For more information, please contact us!

